| Name | |
|---|---|
| Debanjan Saha | saha.deb@northeastern.edu |
| Akhil Krishna Nair | nair.akhi@northeastern.edu |
| Ajay Bana | bana.a@northeastern.edu |
| Venkatesh Gopinath Bogem | bogem.v@northeastern.edu |
| Sai Venkat Madamanchi | madamanchi.s@northeastern.edu |
| Siddharth Banyal | banyal.s@northeastern.edu |
Table of Contents
Introduction
Problem Statement
Speech emotion recognition (SER) is a fascinating application of machine learning that involves analyzing human speech to determine the speaker’s emotional state. It operates on the premise that vocal expressions contain a wealth of emotional information, manifesting in variations in tone, pitch, volume, and speech rate. By capturing and interpreting these acoustic nuances, SER systems aim to bridge the communicative gap between humans and machines, allowing for more intuitive and empathetic interactions across various technological domains.
The primary objective of this project is to develop and implement a machine learning pipeline to help recognize an emotion in a speech in real time. By leveraging advanced machine learning and deep learning models, we aim to enhance the existing emotion recognition, ensuring optimal resource utilization while making accurate emotion classifications of speech.

Methodology
Our approach to developing a speech emotion recognition system will involve collecting a diverse dataset of spoken emotional expressions. We’ll extract salient audio features and train machine learning models to classify these emotions accurately. Key phases will include data preprocessing, feature extraction, model selection, training, and validation. The application of deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), will allow our models to capture the complex patterns inherent in emotional speech.
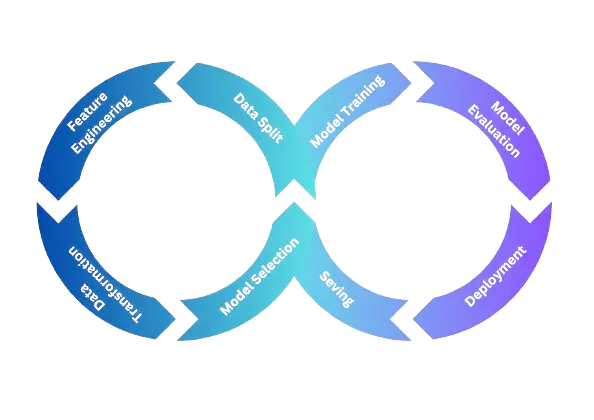

- Data Collection and Preprocessing: Gather a dataset of audio recordings with labeled emotions. Preprocess the audio data to extract relevant features, such as Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), to represent the audio signals.
- Model Selection and Training: Choose appropriate machine learning models for classification, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), or their combinations like Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks (CRNNs). Train these models on the preprocessed audio data.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimization of the hyperparameters of the chosen models to improve their performance. This could involve techniques like grid search or random search.
- Evaluation: Evaluate the performance of your models using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. We may use techniques like cross-validation to ensure robust evaluation.
- Deployment: Once we have a model which is trained and meets the satisfactory levels of performance, we need to consider how to deploy the model. This might involve integrating it into a software application or service.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: After deployment, we need to monitor the performance of our model in the wild and update it as needed to maintain its effectiveness.
- Documentation and Reporting: We should maintain proper documentation of the work thoroughly, including your dataset, preprocessing steps, model architectures, training procedures, and evaluation results. This documentation will be valuable for future reference and for reporting our findings to others.
- Ethical Considerations: We also consider the ethical implications of our work, such as ensuring fairness and avoiding biases in our dataset and models.
Goals
The primary goal is likely to develop a machine learning model that can accurately classify audio signals of human speech into different emotions.

- Improving Customer Experience: SER can be used to analyze customer interactions, such as calls to customer service, to understand customer emotions and improve service quality.
- Enhancing Product Development: It can be used to analyze user feedback on products or services to understand customer sentiments and preferences, guiding future product development.
- Increasing Sales Effectiveness: It can also be used to analyze sales calls or customer inquiries to identify emotional cues and tailor sales strategies accordingly, potentially improving sales effectiveness.
- Monitoring and Improving Employee Well-being: It can also be used to monitor employee interactions, such as in call centers, to identify signs of stress or dissatisfaction and suggest proactive measures to improve employee well-being.
- Personalized Marketing: It can be used to analyze customer responses to marketing campaigns and tailor future campaigns based on emotional responses, leading to more effective marketing strategies.
- Enhancing User Interfaces: it can also be used to develop more intuitive and emotionally responsive user interfaces for applications, improving user experience and engagement.
The source code for our project can be found here: GitHub
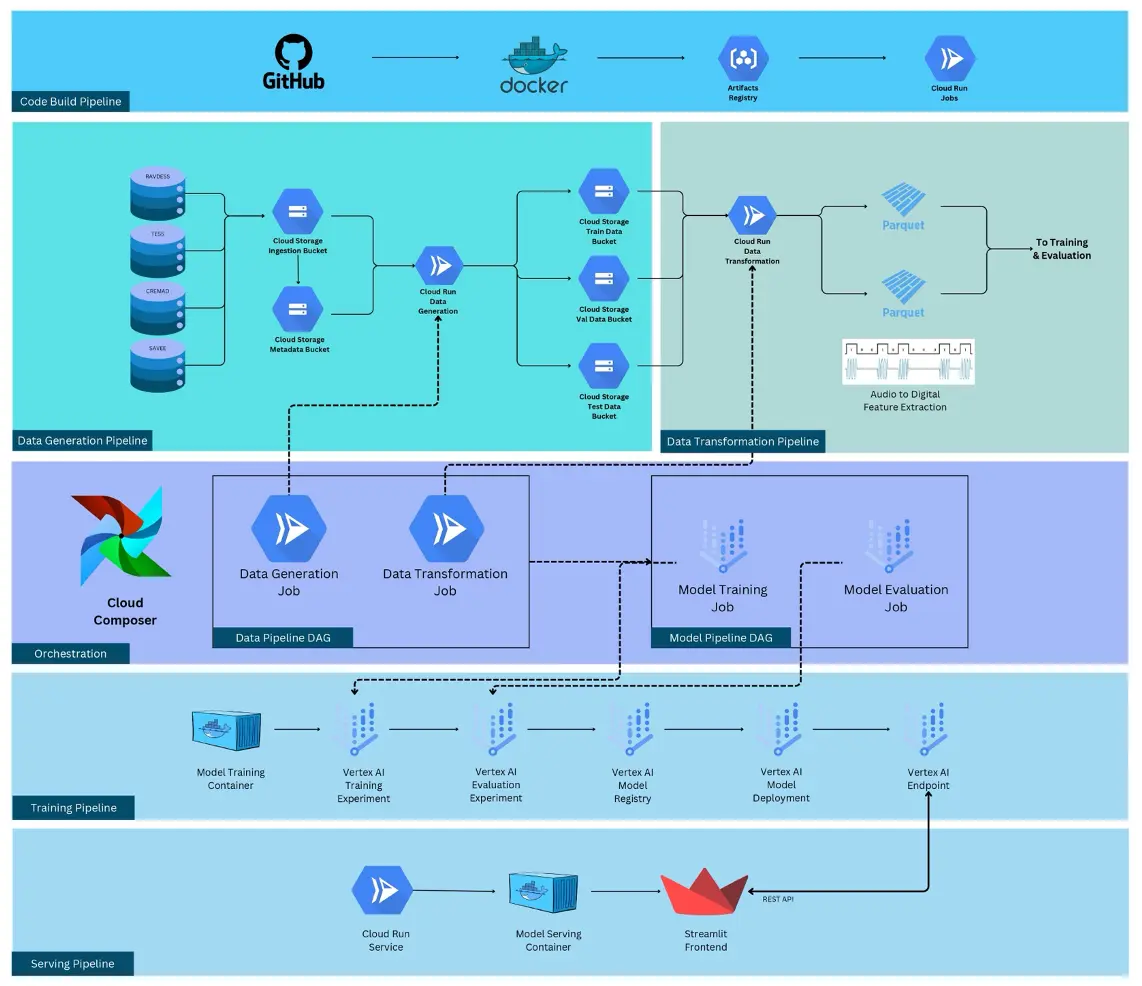
Tools used for MLOps
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Cloud Composer: Used for Airflow orchestration of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) to manage workflow tasks.
- Cloud Run: Used for running jobs triggered by Composer, such as data preparation, transformation, and model training, providing scalability and flexibility.
- Vertex AI: Utilized for model training, deployment, creation of a model endpoint, and monitoring, enabling streamlined machine learning operations.
- Google Cloud Storage: Used as a storage for various objects and artifacts related to the project, experiments and much more.
- Artifacts Registry: Used a repository of Docker containers used to orchestrate microservices as part of the pipelines within GCP.
Project Architecture