Table of Contents
Overview
The Verta-Chatbot project implements a robust Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) system to streamline development, testing, and production deployment processes. This pipeline includes:
- Automated unit and integration testing.
- Seamless containerization and storage in Google Artifact Registry.
- Scalable deployment to Google Cloud Run.
- Integration with LangGraph workflows and external APIs (e.g., OpenAI, HuggingFace).
This document provides a detailed explanation of the project structure, CI/CD workflows, testing integration, and deployment to staging and production environments.
Project Features
- Integrated Workflows:
- LangGraph workflows for pipeline orchestration.
- Automated execution of stages like data ingestion, evaluation, and bias detection.
- Cloud-Native Deployment:
- Containerized deployments via Google Cloud Run.
- Centralized image storage using Google Artifact Registry.
- CI/CD Pipelines:
- Staging and production pipelines with GitHub Actions.
- Integrated testing for application reliability.
- Comprehensive Testing:
- Unit tests for API endpoints, Python workflows, and LangGraph nodes.
- Automated test result reporting.
CI/CD Workflow
The CI/CD pipeline automates the entire lifecycle from testing to deployment.
Integration with GitHub Workflows
The integration of these workflows within the CI/CD pipeline occurs as follows:
- Staging Deployment: The
staging.ymlworkflow runs unit tests, and evaluates the model including the bias detection, to the staging environment. This stage is crucial for real-world testing under controlled conditions. - Production Deployment: The
production.ymlworkflow handles the deployment of the models to the production environment after ensuring that all criteria are met in the staging review. This workflow also triggers the final model training jobs in production, processing new data as needed.
Development Phase
- Activity: Developers push code to branches of the dev branch.
- Details: This phase may include local tests and initial validations before moving the code to a shared environment.
Pull Request Creation
- Activity: Once development is completed in the
devbranch, a pull request is created to merge the changes into thestagingbranch. - Details: This triggers several checks and workflows.
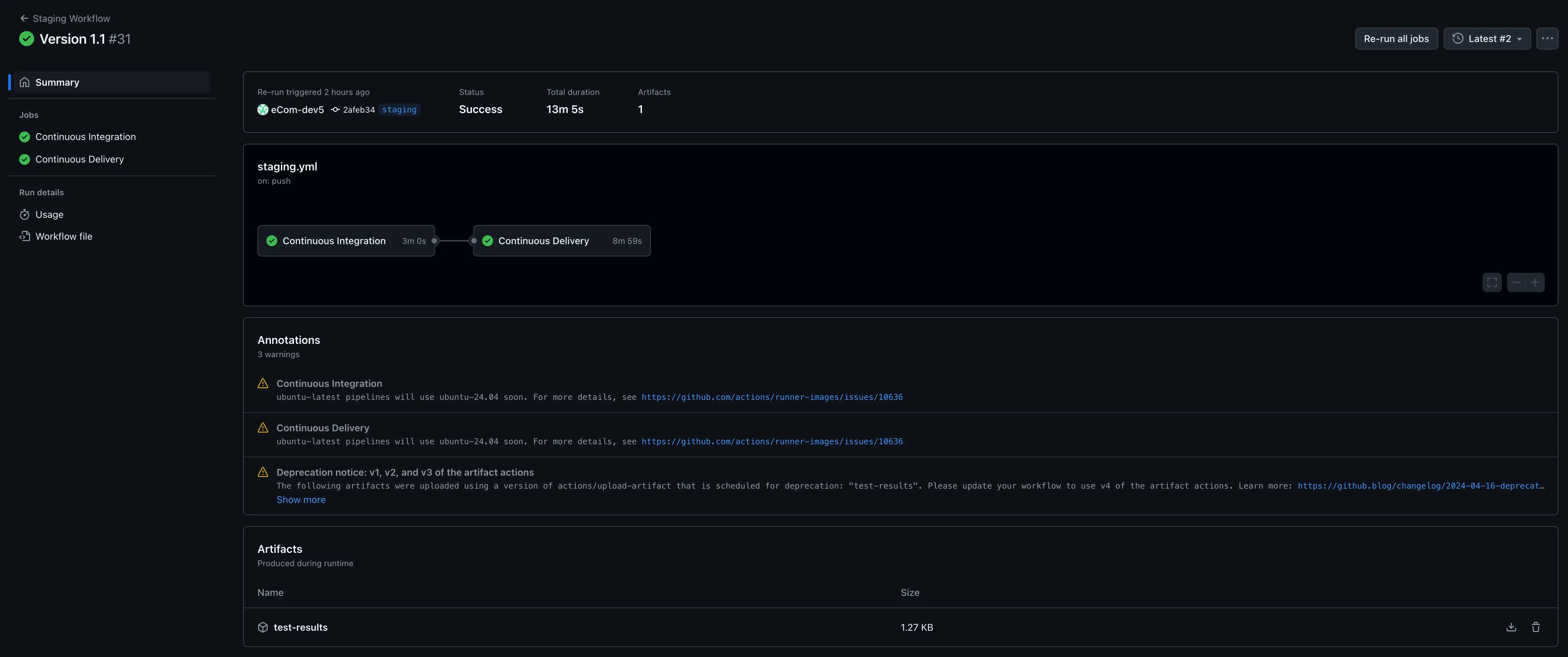
Staging Workflow
File: staging.yml
- Trigger: Pull request from
devto thestagingbranch. - Purpose: Deploys to the staging environment for validation and testing.
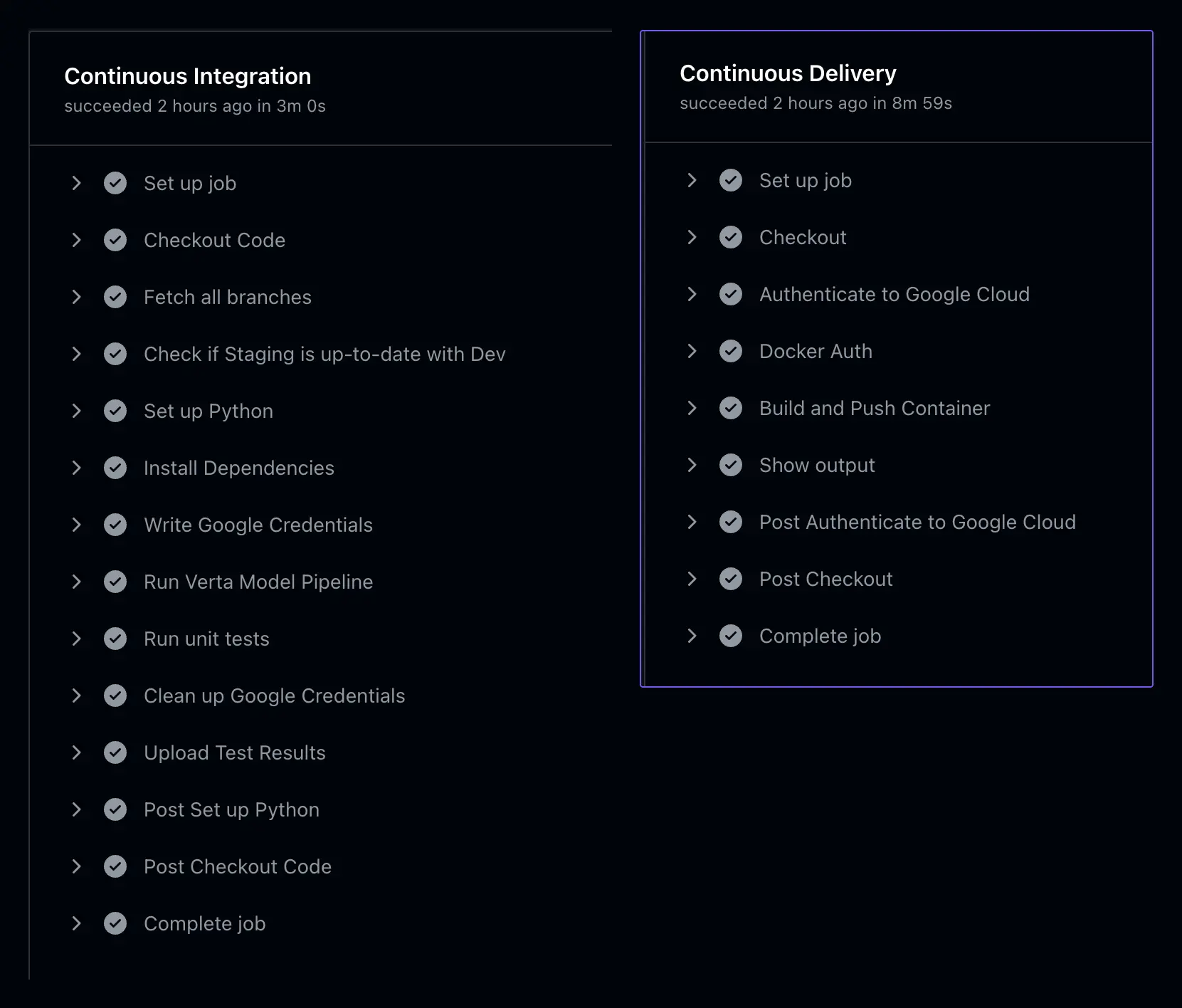
Steps:
- Checkout Code: Pulls the latest changes from the
stagingbranch. - Run Model Pipeline: Execute
main.pyfor model pipelines. Sends alerts and notifications if the metrics are not up to the mark. - Run Unit Tests: Executes unit tests for APIs and pipelines using
pytest. - Build Docker Image: Creates a Docker container for the backend application.
- Push to Artifact Registry: Pushes the containerized application to Google Artifact Registry.
- Deploy to Cloud Run (Staging): Deploys the container to a staging Cloud Run service for testing.
Pull Request Creation
- Activity: Once development is completed in the
stagingbranch, a pull request is created to merge the changes into theproductionbranch. - Details: This triggers several checks and workflows.
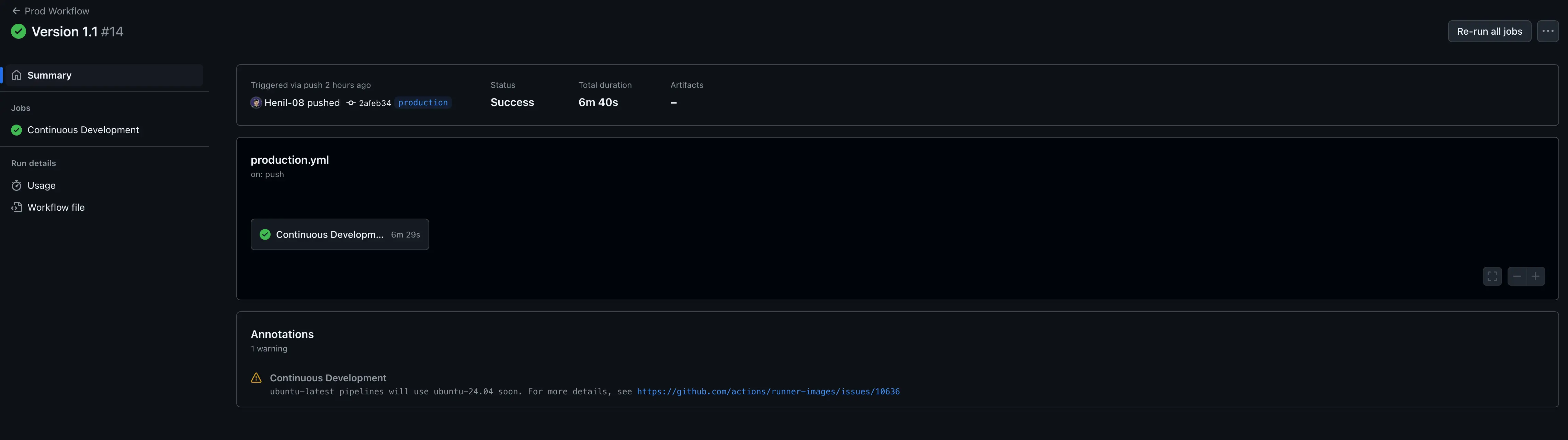
Production Workflow
File: production.yml
- Trigger: Pull request from
stagingto theproductionbranch. - Purpose: Deploys validated code to the production environment.
Steps:
- Sync Validation: Ensures the
productionbranch is in sync with the validatedstagingbranch. - Authentication: Authenticates with Google Cloud using a service account key.
- Deploy to Cloud Run (Production): Deploys the containerized application to the production Cloud Run service.
- Post-Deployment Validation: Ensures the production service is live and accessible.

Artifact Registry and Cloud Run Integration
Artifact Registry
- Build Docker Image: The application is containerized using the
Dockerfiledocker build -t "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/{PROJECT_ID}/{GAR_NAME}/{SERVICE}:{COMMIT_SHA}" -f Dockerfile . - Push to Registry: Pushes the Docker image to Google Artifact Registry
docker push "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/{PROJECT_ID}/{GAR_NAME}/{SERVICE}:{COMMIT_SHA}"
Cloud Run Deployment
- Configuration:
- Cloud Run is configured with the following:
- Memory: 16Gi
- CPU: 4
- Autoscaling: Min 1, Max 10 instances
- Example Deployment Command:
gcloud run deploy {SERVICE_NAME} \ --image "us-east1-docker.pkg.dev/{PROJECT_ID}/{GAR_NAME}/{SERVICE}:{COMMIT_SHA}" \ --region "us-east1" \ --platform managed \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --memory "16Gi" \ --cpu "4"
- Cloud Run is configured with the following: