Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Scoping
- Data Pipeline
- Modeling
- Deployment
- AWS Deployment Setup
- CI/CD
- Monitoring
1. Overview
The modelling pipeline in MedifyAI consists of three key phases:
- HealthcareChatLLM for structured patient symptom collection and emergency detection
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for case-based medical analysis and context retrieval
- OpenBioLLM for interactive patient report analysis
These phases ensure structured medical conversations, accurate retrieval-based analysis, and explainable AI-driven patient insights.
2. RAG Workflow
Below is a high-level workflow of the HealthcareChatLLM and RAG system.
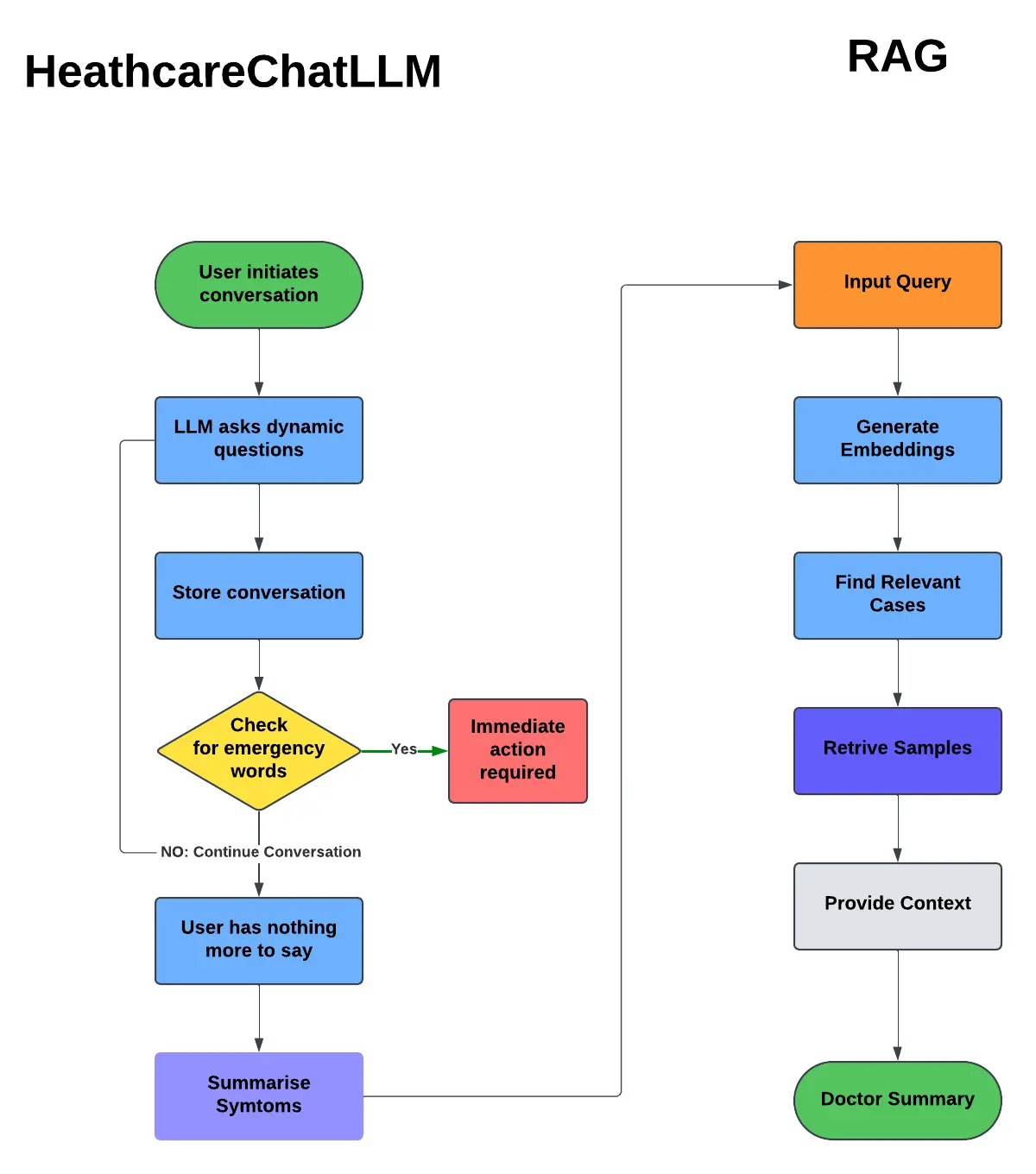
3. HealthcareChatLLM: Medical Symptom Collection
3.1 Purpose
HealthcareChatLLM structures patient interactions by guiding users through a conversation to collect relevant symptoms. It ensures the input data is clear before passing it to the retrieval system. Emergency detection helps in identifying critical medical cases.
3.2 Workflow
- The user initiates a conversation.
- The chatbot asks follow-up questions based on symptoms.
- Conversations are stored and analyzed for context.
- Emergency words are checked, and an alert is triggered if needed.
- If no emergency is detected, the chatbot continues asking relevant questions.
- Once the user has no further input, the system summarizes the symptoms.
4. RAG System: Case-Based Medical Analysis
4.1 Purpose
The RAG model retrieves similar historical cases from the dataset and generates a doctor summary. This improves AI explainability by referencing real-world patient cases for evidence-based recommendations.
4.2 Workflow
- The summarized symptoms are converted into an input query.
- Embeddings are generated for the query using a sentence-transformers model.
- The system finds relevant cases from the vector database.
- The most similar cases are retrieved based on semantic similarity.
- Context is provided, and a doctor summary is generated.
5. OpenBioLLM: Interactive Patient Report Analysis
5.1 Purpose
Once the doctor summary is generated, OpenBioLLM allows patients to ask questions about their reports. This helps users understand their diagnosis better.
5.2 Workflow
- The doctor summary is stored in the patient’s record.
- The patient can ask questions about the report.
- OpenBioLLM extracts information from the summary and provides explanations.
- Follow-up questions can be asked for deeper clarification.
6. Model Tracking and Experimentation
6.1 MLflow Integration
MLflow is used to track all experiments and models, storing training parameters, performance metrics, and artifacts.
- Stores all runs under “healthcare-chat-rag-system”
- Tracks key parameters such as retrieval settings, token limits, and temperature values
- Provides a web interface to compare models
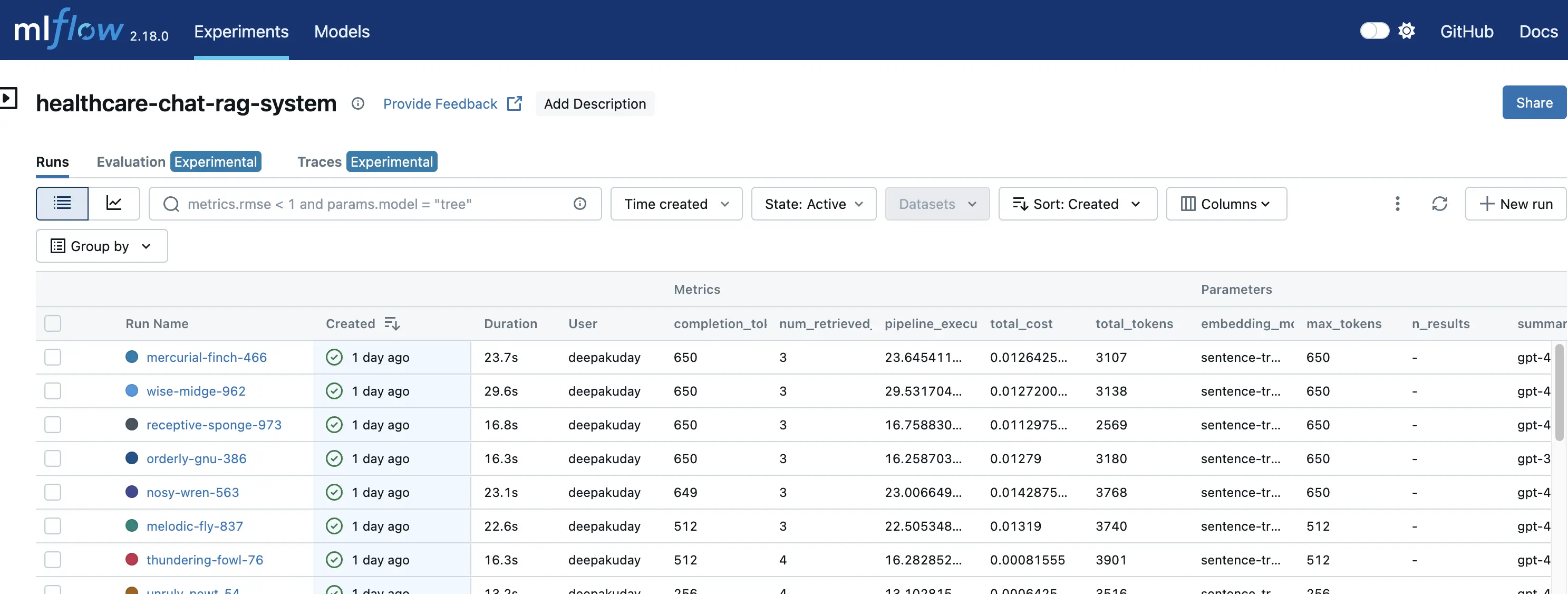
6.2 Best Model Selection
Several experiments were conducted to identify the best-performing model.
| Experiment | Model | Max Tokens | Retrieved Samples | Cost Efficiency | Bias Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1 | GPT-3.5 | 800 | 3 | High | Medium |
| Run 2 | GPT-4 | 800 | 3 | Medium | Low |
| Run 3 | GPT-4o | 800 | 3 | Medium | Lowest |
The final model configuration uses GPT-4o with three retrieved samples, as it provided the best balance of accuracy, cost, and bias minimization.
7. Bias Detection and Evaluation
7.1 Bias Detection
A bias detection system was implemented to ensure fair and unbiased treatment across different demographic groups.
- Evaluates differences in model responses based on gender, age, and prior medical history
- Detects variations in language complexity, urgency levels, and sentiment
7.2 Performance Metrics
The following metrics were used to evaluate model performance:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Retrieval Accuracy | Measures how well retrieved cases match the query |
| Token Cost | Tracks API usage to optimize cost |
| Response Consistency | Ensures structured and logical outputs |
| Bias Score | Measures demographic fairness in model responses |
A similarity threshold of 0.5 was used to determine whether retrieved cases were relevant.
8. Technical Components
8.1 Embedding Model
- Model used: sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
- Embedding dimensionality: 384
- Vector database: Pinecone
8.2 Retrieval Mechanism
- Retrieval strategy: Semantic similarity search
- Similarity metric: Cosine similarity
- Case selection: Top-K most similar cases
8.3 Large Language Models Used
| Phase | Model Used | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| HealthcareChatLLM | GPT-3.5 | Structured symptom collection and emergency detection |
| RAG System | GPT-4o | Context-based medical case retrieval and doctor summary generation |
| OpenBioLLM | OpenBioLLM (LLaMA 3 - 70B) | Interactive patient report explanation |
9. Cost Estimations
The cost estimation for model inference and data retrieval is based on:
| Component | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Embedding generation | $0.02 per 1,000 samples |
| Pinecone database storage | $0.06 per GB per month |
| OpenBioLLM inference (SageMaker) | $1.20 per hour |
| API calls to OpenAI models | $0.002 per 1,000 tokens |
By optimizing embedding dimensionality and retrieval size, API costs are minimized while maintaining accuracy.